If you consume marijuana, you probably familiar with Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol. It also goes by the name Delta-8-THC.
Yep, Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol is the psychoactive ingredient in cannabis that provides the high.
Another compound called Cannabidiol (or CBD) has been making headlines the last few years. This cannabinoid provides a multitude of medicinal benefits without the psychoactive effect. Since CBD does not induce euphoria, “it an appealing option for patients looking for relief from inflammation, pain, anxiety, psychosis, seizures, spasms, and other conditions without disconcerting feelings of lethargy or dysphoria,” according to Project CBD.
But there is another cannabinoid that’s flying under the radar that few people talk about, not even expert tokers. It’s called Delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol, or Delta-8-THC, one of the more than 100 cannabinoids found in the cannabis plant.
Most of the clinical studies have focused on Delta-9-THC and CBD. There is not much research into Delta-8-THC.
RELATED: What Is Marijuana’s THCA And What Does It Do?
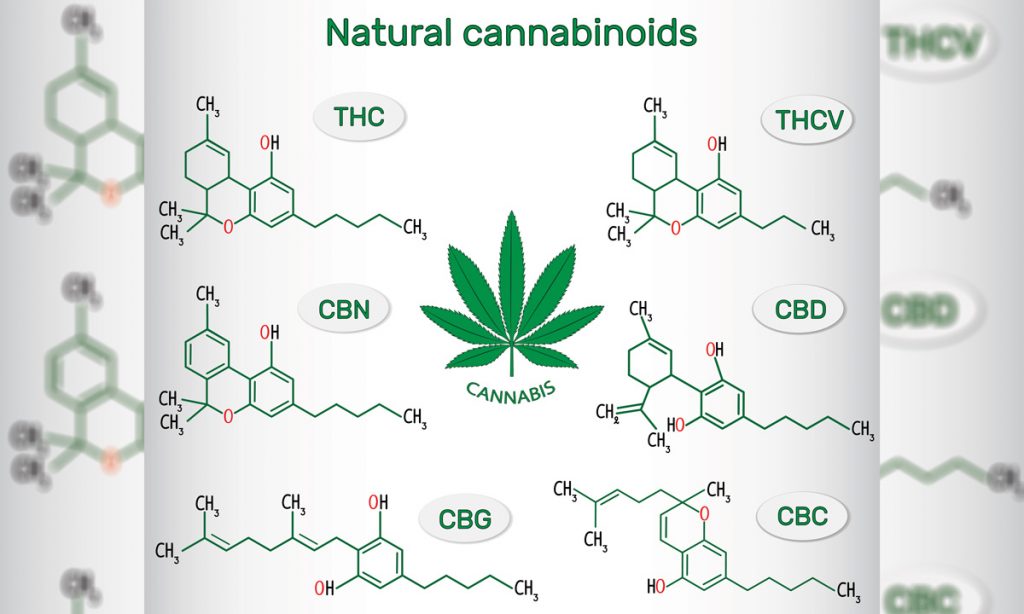
According to the National Cancer Institute, Delta-8-THC is:
An analogue of tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) with antiemetic, anxiolytic, appetite-stimulating, analgesic, and neuroprotective properties.
Let’s break down this definition:
- Antiemetic: A drug used to combat nausea or vomiting.
- Anxiolytic: A drug that fights anxiety or panic.
- Appetite-stimulating: Pretty self explanatory. This is the compound that gives you the munchies. For those with wasting syndrome, this is important to know.
- Analgesic: A class of drugs used to relieve pain. This is a mild form of a painkiller.
- Neuroprotective: Provides support for nerve cells.
That’s an impressive list of medicinal benefits from a relatively unknown compound. More research is needed to verify these qualities, but the prospects look bright. Delta-8-THC does have some psychoactivity, but very little.
SHOP Online THC and CBD Products
From a chemistry standpoint, Delta-8-THC looks nearly identical to Delta-9-THC. Only a few bonding electrons are different. But what it does once it is inside your body is very different.